Pre-Implantation Genetic Testing
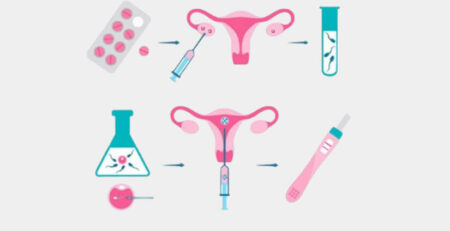
Pre-Implantation Genetic Testing (PGT) is a technique used to test embryos for any known genetic condition of chromosome abnormality (PGD- Pre implantation Genetic Diagnosis) or screen all the chromosomes for any aneuploidy ( PGS- Preimplantation Genetic Screening). This process then enables to select only embryos that are chromosomally normal or unaffected by any disorder. These carefully selected embryos are then used for an IVF cycle, maximizing the chances of a healthy baby.
Pre-Implantation Genetic Testing is suggested for:
- Testing single gene mutation in both parents to avoid passing to the future children.
- If either of the partners is detected with chromosome rearrangement, also known as translocation that could result in genetically abnormal eggs or sperm.
- A couple who has had a pregnancy in the past that has been affected by a chromosomal abnormality
- To test for Down syndrome in women who are over 38 years of age.
- A woman who has had recurrent miscarriages
- A couple who has had repeated IVF failure.
During the procedure of pre-implantation genetic testing, the woman is made to go through a standard IVF cycle. A few cells from each embryo are removed while they are being developed in the IVF laboratory. These cells then sent to be screened for genetic abnormality and based on the report available the unaffected embryo is chosen for embryo transfer.
Why pre-implantation genetic testing?
During the procedure of pre-implantation genetic testing, the woman is made to go through a standard IVF cycle. A few cells from each embryo are removed while they are being developed in the IVF laboratory. This is done by either of the two ways:
- Chromosome testing (Next Generation Sequencing)
This chromosome test allows testing all of the 24 chromosomes in an embryo. This enables and helps in selection of only chromosomally healthy embryos for transfer. - Karyomapping
Karyomapping is done if either of the partner is a carrier of a serious single gene disorder like huntington’s disease, cystic fibroids, thalassaemia, fragile-X, BRCA1/BRCA2 (hereditary breast or ovarian cancer). This test enables in identifying the embryos that are NOT affected by the single gene disorder, thus preventing the condition to be passed on to the future children.