How Fibroids Affect Fertility and Pregnancy
The journey of family planning and the experience of pregnancy is not the same for everyone. For some ladies, it often brings various challenges, one of which is fibroids. These non-cancerous tissue growths that develop in the uterus are particularly common among women, especially during the years they are most fertile.
While many women with fibroids experience healthy pregnancies, it’s not always easy. These growths can sometimes pose challenges to fertility and the overall journey to motherhood. But understanding what fibroids are, their types and the impact of fibroids in pregnancy can help you move smoothly with your pregnancy journey. Keep reading!
What are Fibroids?
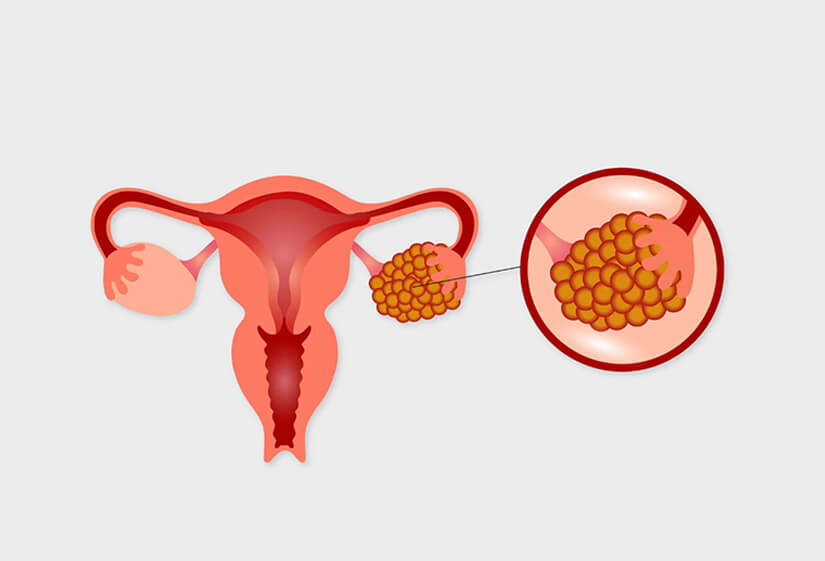
Uterine fibroids, medically known as leiomyomas or myomas, are non-cancerous growths that arise from the muscle tissue of the uterus. They vary greatly in size, ranging from tiny seedlings, undetectable to the human eye, to bulky masses that can stretch and enlarge the uterus.
Here is an interesting fact about fibroids. Fibroids are most prevalent in women in their 30s and 40s, but they can occur at any age during a woman’s reproductive years. Studies show up to 80% of women develop them by age 50.
The best part is that these growths are not typically associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and rarely develop into cancer.
The exact causes of fibroids are unknown, although several factors, such as hormones and genetic changes, seem to be the reasons for fibroids in pregnancy.

Types of Fibroids
Based on their location, fibroids are classified into three different types: submucosal fibroids, intramural fibroids and subserous fibroids.
Submucosal Fibroids: Submucosal fibroids are the least prevalent but most likely to disrupt fertility. They are located in the uterine cavity. They may block embryo implantation by extending into the uterine cavity. Their presence can also change the shape and size of the uterine cavity, making fertilization and pregnancy maintenance more difficult.
Intramural Fibroids: These fibroids in pregnancy develop within the uterine wall. Their impact on fertility largely depends on their size. Larger intramural fibroids, especially those exceeding 4-5 centimetres, can distort the uterine cavity, similar to submucosal fibroids, potentially hindering implantation and affecting the chances of pregnancy.
Subserosal Fibroids: Subserous fibroids, which grow on the outer uterine wall, have no direct influence on fertility. They can become quite large and may cause other health issues. However, their location outside the uterine cavity doesn’t typically interfere with implantation.
Symptoms of Fibroids
When it comes to fibroids, there is a little bit of confusion because the fibroid symptoms vary from woman to woman, depending on their size and location. Here are the most common symptoms you might encounter:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pain or heaviness in the pelvic area
- Enlargement of the abdomen
- Pain during intercourse
- Lower back pain
- Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder
- Infertility or miscarriage
- Constipation

Impact of Fibroids on Fertility
Fibroids are a common source of anxiety for women, particularly those who are trying to conceive. You might be thinking, do fibroids interfere with fertility? If yes How? Also how do fibroids in pregnancy behave? Let’s see.
Effect of Size and Location: Submucosal and large intramural fibroids are known to interfere with fertility. They may block the fallopian tubes, disrupting egg and sperm movement. Fibroids can also cause uterine lining problems, making it less susceptible to embryo implantation.
Cervical Fibroids: Fibroids growing in or around the cervix block the uterus’s entrance, making it difficult for sperm to reach their destination and fertilize an egg.
Altered Uterine Structure: Fibroids, depending on their size and location, can change the shape and size of the uterus. This changed uterus shape poses challenges for implantation and increases the risk of miscarriage.
Uterine Lining and Blood Supply: Do you know fibroids can impact the blood flow to the uterine lining? Large fibroids can block the blood supply path, affecting its quality and thickness. It can result in infertility.
Blocked Fallopian Tubes: Fibroids that obstruct or push on the fallopian tubes can interfere with proper fertilization. The inability of eggs and sperm to meet may reduce the chance of fertilization.
Impact of Fibroids on Pregnancy
While most women sail through pregnancy safely with fibroids, around 10-30% experience complications, mainly pain, especially with larger fibroids in pregnancy. Fibroids may increase additional issues during pregnancy and delivery. These may include:
Complications During Pregnancy: Fibroids can increase the risk of certain complications during pregnancy. These include:
- Pain and Discomfort: Large or growing fibroids can press on surrounding organs and tissues, leading to pain, pressure, or cramps during pregnancy. This pain will increase the chances of uterine contractions, leading to early delivery.
- Breech Birth: Fibroids may disrupt the baby’s placement in the uterus, increasing the probability of breech delivery, in which the infant is born feet first rather than head first.
- Placental Abruption: This condition, where the placenta detaches from the wall of the uterus before childbirth, can be more common in women with fibroids.
Impact on Fetal Growth: Large fibroids in pregnancy may block fetal development by taking up uterine space or altering blood flow.
Cesarean Section (C-Section): Fibroids can increase the chances of the baby being in a breech position or other problems during delivery. In that case, you may need a C-section.
Miscarriage: Some research indicates that fibroids, particularly submucosal fibroids, may increase the likelihood of miscarriage in the first or second trimester.
Postpartum Hemorrhage: Women with fibroids are more likely to experience excessive bleeding after giving birth.
Treatment for Fibroids
Are you wondering if it is possible to treat fibroid symptoms before conceiving? Can I get pregnant with fibroids? Good news, ladies. Early detection of fibroids can allow for more conservative treatment options that preserve fertility. Regular gynaecological examinations and imaging tests like ultrasounds can help in early diagnosis and treatment.
Let’s explore these options.
Medication: Various medications can help manage fibroid symptoms. These treatments might shrink fibroids or control symptoms like heavy menstrual bleeding. However, the response to medication varies, and not all fibroids will respond to medical therapy.
Hormonal contraceptives and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa) are the most common medications used to manage fibroids. While hormonal contraception is often used to prevent excessive menstrual flow and has no impact on fibroids, GnRHa medicines can help reduce the size of fibroids.
Laparoscopic Myomectomy: If you are planning to conceive, laparoscopic myomectomy is a viable treatment option for fibroids in pregnancy. This surgery helps to remove fibroids without taking out the healthy tissue of the uterus. It is best for women who wish to have children after treatment for their fibroids or who wish to keep their uterus for other reasons. You can become pregnant after myomectomy. But if your fibroids were entered deeply into the uterus, you might need a cesarean section to deliver. Myomectomy can be performed in many ways laparoscopy or hysteroscopy. The type of surgery that can be done depends on the type, size, and location of the fibroids. After a myomectomy, new fibroids can grow and cause trouble later.
Other Treatment Options to Deal With Fibroids
Hysterectomy: If you have significant fibroids symptoms or large fibroids, and family is completed, hysterectomy is the best option to get relief. If the fibroids are large, a woman may require a hysterectomy, which includes removing the uterus through an incision in the abdomen.
Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is a minimally invasive alternative to surgery for treating symptomatic uterine fibroids. UAE can significantly reduce the size of fibroids, leading to symptom relief like reduced bleeding, pain, and pressure. So, how does it work?
A thin tube is inserted into the blood vessels that feed the fibroid. Tiny gel particles are then injected, blocking the blood flow and causing the fibroid to shrink.
Now, who can get uterine artery embolization treatment?
- Women who have fibroids causing heavy bleeding, pain, or pressure
- Don’t want a hysterectomy
- Don’t plan to have children in the future
Tailored Treatment Plans: Since each case is unique, treatment plans should be personalized based on the size, location, and fibroids symptoms, as well as the woman’s age, overall health, and desire to have children.
If you are dealing with Fibroids, it’s better to reach the IVF centre in Delhi to find other alternatives to conceive.
Conclusion!
While fibroids are common, they do not mean the end of one’s reproductive journey. Understanding the types of fibroids and their potential impact on fertility and pregnancy can help you find the treatment option and enjoy a happy pregnancy.
If you are looking for fibroids in pregnancy treatment, book your consultation with Dr Rhythm Gupta, an experienced infertility specialist in Delhi. She will guide you on the impacts of fibroids on your pregnancy or fertility and provide a tailored treatment plan so that you can fulfil your dreams of starting a family.