How Does Tuberculosis Affect Female Fertility?
Tuberculosis, or TB, is an old illness that continues to pose a severe health issue, particularly in developing nations such as India. This infectious disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, typically affects the lungs but can also spread to other areas of the body, like genital organs, and impact one’s ability to conceive.
Yes, you read it right. Tuberculosis can affect your fertility. But don’t panic! Understanding what tuberculosis is, tuberculosis treatment, and how it affects your fertility can help you manage the condition and increase your chances of conceiving naturally.
Let’s explore!
What is Tuberculosis?
First and foremost, we understand the basis of tuberculosis.
When we think of tuberculosis, we often imagine a lung-related disease characterized by coughing and difficulties with breathing. This primary form, known as pulmonary tuberculosis, is indeed the most common manifestation.
However, many of us don’t know that tuberculosis is dormant, which means tuberculosis bacteria in the body may go into sleep mode for a long time, even decades. This form doesn’t show symptoms immediately. But under certain conditions, particularly when the immune system is compromised, these bacteria can become active and start causing problems. One of the major issues they cause is affecting your fertility.
Now, you would ask how these lung-related bacteria can affect fertility. These tiny bacteria enter the blood, and through the bloodstream, they travel to the genital tract, causing genital tuberculosis. In females, it affects the fallopian tubes and ovaries. In males, it targets reproductive organs like the testis, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles and prostate.
You can experience pain in the pelvis, irregular menstrual cycles, abdominal swelling, bleeding after sexual intercourse, weight loss and fatigue with uterine tuberculosis. In males, it can cause pain in the testicles, swelling or lumps and a sensation of heaviness in the testicles.
Therefore, diagnosing to find effective tuberculosis treatment on time is essential.
Effect of Tuberculosis on Female Fertility
The spread of tuberculosis to the female genital tract is a serious problem because it can directly lead to infertility. Once bacteria have settled in the reproductive organs, they may cause trouble in many ways. The most common female fertility causes include:
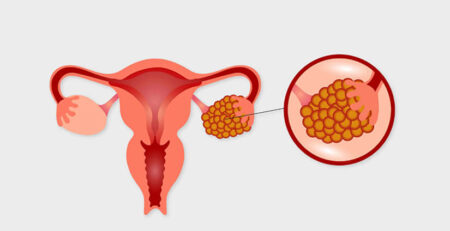
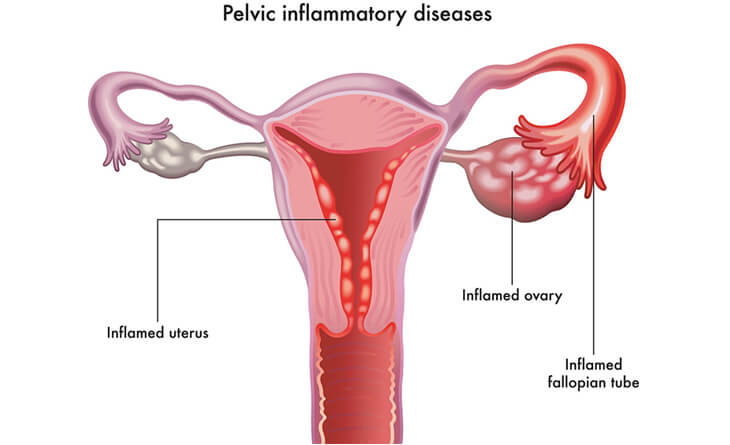
Tubal Blockage: The fallopian tubes play an important role in fertility because they allow the egg to travel from the ovary to the uterus. However, tuberculosis can cause inflammation and scarring in these tubes, leading to blockages. This not only slows the egg’s journey but also increases the risk of ectopic pregnancies, where the embryo implants outside the uterus.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Tuberculosis can cause a severe form of PID, an infection of the female reproductive organs. This condition can cause chronic pelvic pain, irregular menstrual cycles, and significant damage to the reproductive organs, compromising fertility chances. In that case, you need to consult IVF specialist in Delhi for effective treatment.
Tuberculin Masses: The presence of tuberculosis can lead to the formation of tuberculin masses in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. These masses can disrupt the normal function of these organs, affecting ovulation and egg transportation.
Impact on Uterine Lining: One of the most serious effects of genital tuberculosis is on the uterine lining. Tuberculosis infection can cause the endometrium to stay the bacteria, leading to abnormal bleeding. You can experience scanty periods or, conversely, heavy bleeding. Additionally, it can make the lining too thin, an unfavourable condition for embryo implantation, leading to infertility and challenges in pregnancy.
Challenges in Fertility Treatment: Along with female fertility causes and challenging pregnancy, tuberculosis bacteria can interfere with fertility treatment effectiveness, making it more difficult to achieve pregnancy. In severe cases, you may need to postpone your fertility treatment until the infection is under control.
Impact on Ovarian Function: While the fallopian tubes and endometrial tissue are the target organs of genital tuberculosis, the ovaries are also not immune to the effects of this disease. It can interfere with ovarian functions, ending their ability to produce eggs and hormones necessary for reproduction.
Increase Risk of Miscarriages: Tuberculosis compromises the health and integrity of the endometrium, creating an environment that’s less than ideal for an embryo to implant and grow. In those cases, the chances of miscarriage increase.
We have seen that tuberculosis can compromise your dream of having your own family. Therefore, if you are experiencing any signs of tuberculosis, consult your doctor before it’s too late and start tuberculosis treatment.
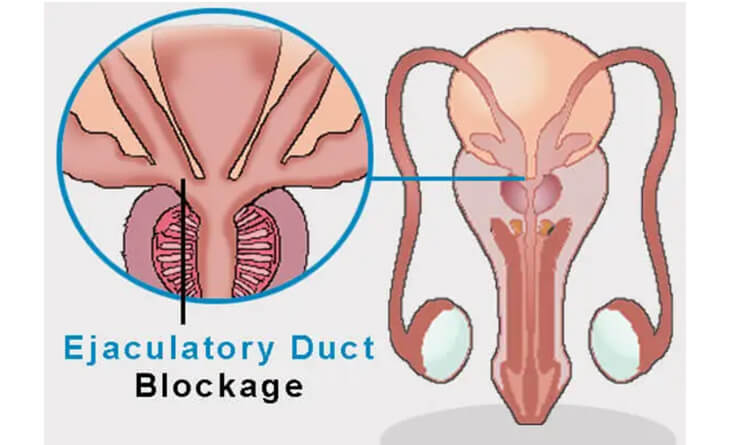
Effect of Tuberculosis on Male Fertility
While tuberculosis majorly affects the female genital organ, it also extends its reach to male reproductive health. The way tuberculosis affects male fertility can be both direct and indirect, often leading to long-term consequences. Let’s see how tuberculosis affects male fertility.
Chronic Infection: Tuberculosis in males can increase the risk of infection in reproductive organs, leading to infertility or ejaculation issues in males.
Impact Semen Parameters: Tuberculosis can indirectly affect semen parameters, including sperm count, motility, and morphology, making it difficult to fertilize an egg successfully.
Blockage of Reproductive Ducts: Similar to females, tuberculosis can cause blockages in the male reproductive ducts, including the epididymis and vas deferens, which are crucial for sperm transport. Blockages in these areas can lead to conditions like obstructive azoospermia, where sperm is produced but cannot be present in the ejaculate.
That’s why it is essential to get tuberculosis treatment before it’s too late.
How to Diagnose Genital Tuberculosis?
Genital tuberculosis is challenging to diagnose because it does not show any signs until you try to conceive or have difficulty in intercourse or getting pregnant. Additionally, genital tuberculosis can sometimes be misdiagnosed as other reproductive system disorders, such as menstrual irregularities or endometriosis.
Therefore, your fertility doctor will perform a thorough physical examination and ask for your medical history, including your tuberculosis history, tuberculosis exposure or HIV and any tuberculosis treatment that you are taking, so that your doctor can find the root cause to provide you with a customized treatment plan.
Other tests to diagnose genital tuberculosis may include:
Imaging Testing: In order to detect any abnormalities in the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, your doctor or IVF specialist in Delhi may prescribe ultrasound, X-ray, Tubal test HSG, CECT. Sometimes, an ultrasound is also recommended.
Laparoscopy: Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgery that allows doctors to have a direct visual examination of your pelvic cavity. During this procedure, small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera and light) to visualize the pelvic cavity and identify tuberculosis lesions on the reproductive organs. Laparoscopy also helps assess the extent of internal damage and obtain tissue samples for biopsy.
Biopsy: In a biopsy, a small tissue sample is taken from the affected organ and examined under the microscope. In female genital tuberculosis, tissue samples can be taken from the endometrium, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs, and a histopathological examination of these samples is done to confirm the presence of tuberculosis.
Bacterial Cultures: Bacterial culture is another type of examination that helps confirm which type of bacteria impacts your reproductive organs. This information is crucial for tailoring the appropriate tuberculosis treatment or fertility treatment.
These diagnostic tools provide a comprehensive approach to determining genital tuberculosis, assessing its impact on fertility, and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Treatment for Genital Tuberculosis
Do you know that many changes caused due to genital tuberculosis are irreversible? In some cases, the tubal blockage and scarring can be corrected with a successful treatment. Here, a comprehensive diagnosis comes into play. Your doctor will identify the causes and prescribe the most effective tuberculosis treatment and fertility treatment. Some of the treatment options to improve reproductive health include:
Anti-Tuberculosis Therapy (ATT): Anti-tuberculosis therapy is the cornerstone of female genital treatment, similar to the technique used for pulmonary tuberculosis. ATT involves a regimen of specific drugs, and the duration and combination of these medications are tailored based on the severity and extent of the disease.
Surgical Intervention: In some cases, when significant scar tissues are the major female fertility causes, surgical interventions are used. This could range from laparoscopic and hysteroscopic guided procedures to remove scar tissue to more extensive surgeries depending on the level of damage. It’s about repairing and restoring as much function as possible.
Fertility treatment: If you are planning to concieve with genital tuberculosis, it is prudent that the restoration of the anatomy is doen surgically and the ATT treatment is taken before any kind of fertility treatment like IUI/IVF is offered. In severe cases of blocked tubes where the medical treatment doesn’t help, using IVF (in vitro fertilization) is the best option as it bypasses the egg release and fertilization process in case of damaged fallopian tubes. In this procedure, ovaries are stimulated to produce enough eggs that are aspirated and mixed with the sperm to fertilize. After that, the embryo is implanted in the uterus lining. Consult with the best IVF specialist in Delhi for a successful outcome in first attempt.
Conclusion!
Female genital tuberculosis is a silent but major health concern. Its influence on fertility, as well as the difficulties in diagnosing and treating it, makes it an urgent priority for women’s health. Awareness, early diagnosis, and proper tuberculosis treatment are essential for controlling FGTB and limiting its impact on women’s reproductive health.
If you are struggling to convince even after trying for a long time, schedule your consultation with Dr Rhythm Gupta, an experienced fertility specialist in Delhi and fulfil your dream of starting a family.