What is The Best Age to Freeze Your Eggs?
Dreaming of starting a family is a common goal, but sometimes, life’s timing doesn’t align with your plans for parenthood. Additionally, health issues might pose challenges to conceiving naturally within your planned timeline. Thankfully, advancements in fertility treatments offer a solution, and egg freezing is one of them.
Opting to freeze your eggs opens up the possibility of deciding when you are ready to start your journey towards motherhood, rather than being bound by the biological clock’s ticking. However, there are several factors, including your age, that you need to consider when exploring egg freezing as an option. Let’s understand how your age affects your ability to freeze eggs so that you can make an informed decision.
The Relation Between Age and Egg Quality
First, you must understand that egg quality and quantity decrease as you age. Let’s understand it.
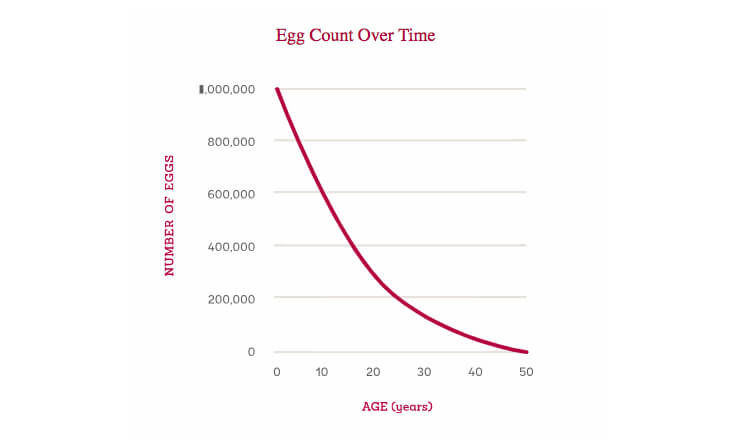
Girls are born with a fixed number of eggs, usually around 1 to 2 million. However, this number drops to about 300,000 to 400,000 eggs by the time a girl reaches puberty. And not all of these will be used in a woman’s lifetime. With each menstrual cycle, a woman loses about one thousand eggs, but only one (or occasionally more in the case of multiple births) has the chance to be fertilized.
As women age, the decline in egg reserve accelerates, especially after age 35. This decrease isn’t just in the number of eggs but in their quality.
Why does this decline happen?
As women get older, the performance of their ovaries starts to decline. This reduction is one due to falling egg number and second due to ovarian ageing and rise of FSH and LH hormone.
Under normal conditions, FSH and LH work together to ensure that a healthy egg develops and is released throughout each menstrual cycle, which is essential for fertility. However, with age, the ovaries become less responsive to these hormones. This decreased responsiveness indicates that hormonal signals that formerly ensured the normal growth and release of eggs are less efficient.
The impact of this reduced ovarian response is dual in the process of Egg Freezing. First, fewer eggs attain full development. Second, the total number of eggs that are mature decreases over time. This combination of factors, depleted egg supplies, reduced responsiveness to hormones, and decreased release of mature eggs substantially influences a woman’s fertility as she matures.
The Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) test and a scan to count the antral follicles determines the egg reserve level for egg freezing. Produced directly by ovarian follicles, AMH levels in the blood provide valuable insights into a woman’s fertility potential. Higher levels of AMH generally suggest a higher number of remaining eggs, whereas lower levels may indicate a reduced ovarian reserve. As the age increases the AMH levels fall.
A significant aspect of this decline in egg reserve and egg quality is an increased likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities in older eggs. One of the most common types of these abnormalities is aneuploidy, which occurs when eggs contain an abnormal number of chromosomes.
Normal human cells, including egg and sperm cells, should have 23 pairs of chromosomes, totalling 46. However, when aneuploidy disrupts this balance, leading to either more or fewer chromosomes in the egg. This imbalance can have a significant impact on fertility and child health. How?
When an egg with an abnormal number of chromosomes is fertilized, it can lead to several outcomes. One possibility is the development of conditions like Down syndrome, which is characterized by an extra copy of chromosome 21. Such chromosomal conditions can affect a child’s physical and cognitive development significantly.
Moreover, the presence of aneuploidy increases the risk of miscarriage. The body often recognizes the chromosomal imbalance as a signal that the embryo may not be viable, leading to the natural termination of the pregnancy. This could be the one reason why the rate of miscarriages is higher among older women.
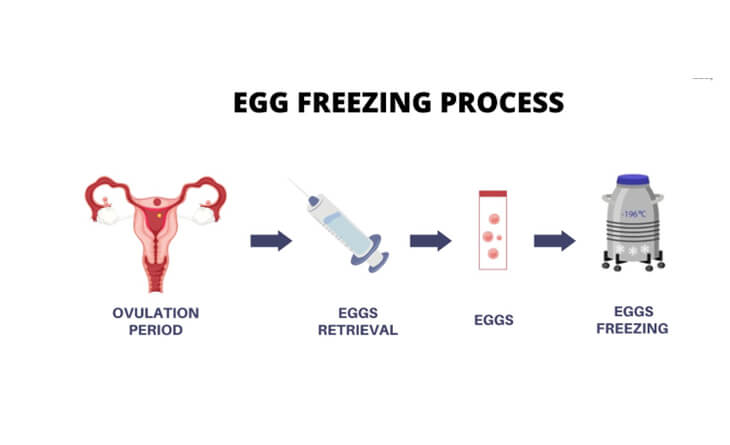
Best Age for Egg Freezing
With the abovementioned condition, what is the best age for egg freezing? Well, there is no definite answer to this. But when considering egg freezing, the rule of thumb is the earlier, the better.
The younger you are, the more likely you are to freeze a larger number of high-quality eggs because younger eggs are genetically normal, have a better chance of surviving the freeze-thaw cycle, a key component of the egg-freezing process. Thawing, or de-freezing the eggs, is critical for ensuring the eggs remain viable for fertilisation, and younger eggs excel in this aspect.
Now, you may be curious about how many eggs should be frozen and at what age this should ideally happen. While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, fertility experts, such as those at leading IVF centres, suggest maximising your chances of egg freezing before turning 30. The recommendation is based on the normal reduction in fertility that occurs with aging. When you are younger, you have good-quality eggs; you need fewer eggs to freeze. However, the quality gets compromised with age, and you need more eggs for the freezing process.
For better understanding, consider the following table that outlines the recommended numbers of eggs to freeze based on age:
| Age | Recommended Number of Eggs to Freeze for at least 1 child | Probability of Live Birth After IVF with frozen eggs |
| <35 | 9 – 12 | 60 – 80% |
| 35-37 | 14 – 16 | 60 – 78% |
| 38-42 | 35 – 45 | 54 – 68% |
| >42 | 50+ | 60 – 70% |
For example, if you’re 34 years old, aiming to freeze around 10 eggs of the best egg quality might increase your chances of a successful pregnancy. To assist with planning, numerous online calculators are available to estimate the number of eggs you might consider freezing.
Additional Consideration for Future Pregnancy
Egg freezing is a significant advancement in fertility preservation, allowing women to delay motherhood until a time that suits them better. However, egg freezing does not ensure a successful pregnancy. Multiple factors might affect the success of pregnancy when using frozen eggs.
Semen Parameters: Semen parameters refer to various aspects of a male’s semen quality, which are essential in determining the likelihood of fertilizing an egg and achieving a successful pregnancy. These parameters include:
- Sperm Count
- Sperm Motility
- Sperm Morphology
Embryo Quality: When a couple uses frozen eggs for pregnancy, the male partner’s sperm is combined with the thawed eggs for fertilization. This fertilized egg undergoes a cell division process and forms the embryo. The semen’s characteristics directly influence the health and viability of the resulting embryos. High-quality embryos are crucial for implantation and a successful pregnancy.
Uterine Health: The condition of the woman’s uterus at the time of embryo transfer is vital. Factors such as the thickness of the uterine lining and the presence of uterine abnormalities like fibroids or polyps can influence the implantation of embryos and the success of the pregnancy.
Health and Lifestyle Factors: Both partners’ overall health, lifestyle choices, and age when using frozen eggs can influence pregnancy success. Healthy habits and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol can improve outcomes.
Therefore, before proceeding with fertilization, the IVF specialist at the best IVF centre in Delhi conducts a comprehensive semen analysis and determines the need of any semen selection technique. This helps in identifying any potential issues that could affect the chances of fertilization and pregnancy.
How are Frozen Eggs Used?
Using frozen eggs for fertilization is a multi-step process that involves thawing the eggs, fertilizing them, and then transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus.
Embryologist at the IVF centre carefully thaw the frozen eggs to bring them back to a state suitable for fertilization. This step is delicate, as not all eggs may survive thawing.
After that, the thawed eggs are fertilized in a laboratory setting. This technique involves injecting a single sperm directly into each egg, increasing the chances of fertilization.
After fertilization, the embryos are monitored in the laboratory for several days. The best embryos are selected for transfer based on their development and quality. Embryo grading assesses the embryos’ appearance and growth rate and helps make this decision. The IVF Centre in Delhi prepares the woman’s uterus for implantation through hormone treatments that mimic the natural menstrual cycle.
One or more embryos are transferred into the woman’s uterus through a thin catheter inserted through the cervix. Approximately two weeks after the embryo transfer, a pregnancy test is conducted to check for pregnancy.
Wrapping Up!
Egg freezing can be a valuable tool for women seeking to manage their fertility timelines. However, it’s essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the factors involved. By making informed decisions and seeking professional guidance, you can navigate this journey with confidence and hope.